Get all the latest news on coronavirus and more delivered daily to your inbox. Sign up here.
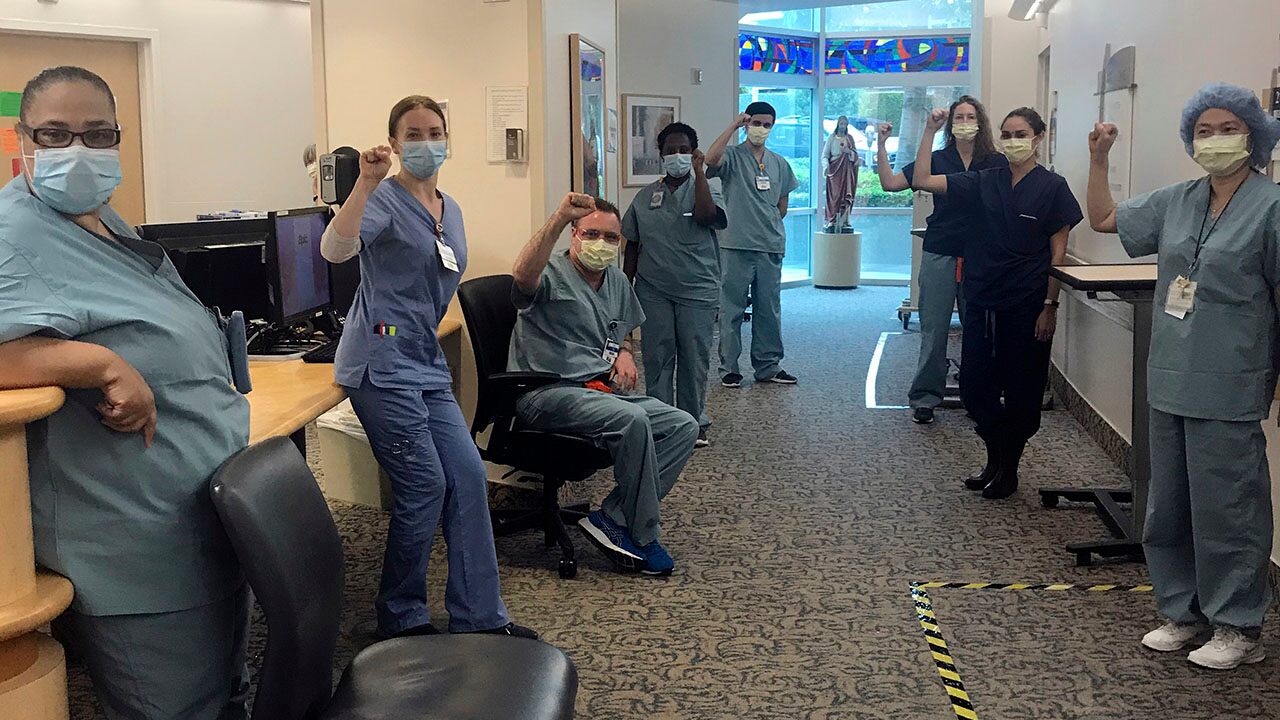
Several Southern California nurses were suspended after they refused to enter coronavirus patient’s rooms without N95 respirator masks, the National Nurses Union said this week.
Mike Gulick, who is one of the suspended nurses, told the Associated Press he’s been extremely careful about not bringing the virus home to his wife and 2-year-old daughter, but said the administrators at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in Santa Monica told nurses N95 masks weren’t necessary and didn’t provide them.
Michigan ER nurses stage sit-in over ‘unsafe patient load,’ told to leave amid coronavirus outbreak
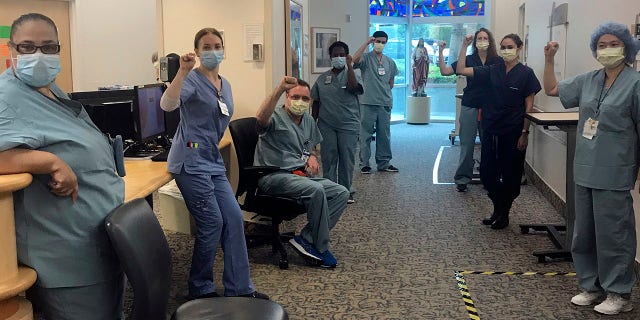
In this image provided by Lizabeth Baker Wade, nurses at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in Santa Monica, Calif.(Lizabeth Baker Wade via AP)
Gulick said the breaking point for him was when a nurse on his ward tested positive for the virus last week and the next day doctors doing rounds asked them why they weren’t wearing N95 masks and said they should have better protection.
The 10 nurses will remain on paid leave pending an investigation from human resources, the union said.
N95 masks filter out about 95 percent of airborne particles, including those too small to be stopped by regular masks.
Gulick’s wife, who is a nurse at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center on the other side of town, not only wears an N95 mask while doing her job but also layers it with another respirator.
Health care workers across the country have been forced to improvise due to widespread shortages of personal protective equipment amid the pandemic.
The virus is especially dangerous for medical professionals since it spreads through respiratory droplets in the air and from bodily fluids transmitted by a cough or sneeze, for example.
Although CDC guidelines don’t require N95 masks for health care professionals treating coronavirus patients, many hospitals are opting to use them because of the highly contagious nature of the virus.
At least 9,200 health care workers have been infected so far, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said Wednesday.
‘We are so grateful to the heroic work our nurses perform each day and will not let the actions of a few diminish the appreciation we have for all our nurses and their commitment to our community,” Providence Saint John’s told FOX 11 in a statement. “Saint John’s cherishes its nurses and is taking precautions sanctioned by leading world, national, state and local health agencies to ensure their safety — the same protocols followed by most hospitals around the country. We have been working for weeks to increase access to PPE and also activate our own local reprocessing centers.”
St. John’s said it is expanding usage of N95 masks for employees caring for coronavirus patients.
“It’s no secret there is a national shortage, and depleting our supply is not an option knowing COVID-19 will remain in our community for weeks and months to come,” the statement said.
On Wednesday, nurse unions in New York, Massachusetts, Michigan, Illinois, California, and Pennsylvania scheduled actions at their hospitals over the lack of protective equipment and posted on social media using hashtag “PPEoverProfit.”
CLICK HERE FOR COMPLETE CORONAVIRUS COVERAGE
The Associated Press contributed to this report.